Adaptive Manufacturing: Personalized Production at Scale
Revolutionizing the industrial landscape, adaptive manufacturing is reshaping how businesses approach production. This innovative methodology combines flexibility, customization, and efficiency to meet evolving consumer demands while optimizing resource utilization. As markets become increasingly dynamic, companies are turning to adaptive manufacturing to stay competitive and responsive in an ever-changing business environment.
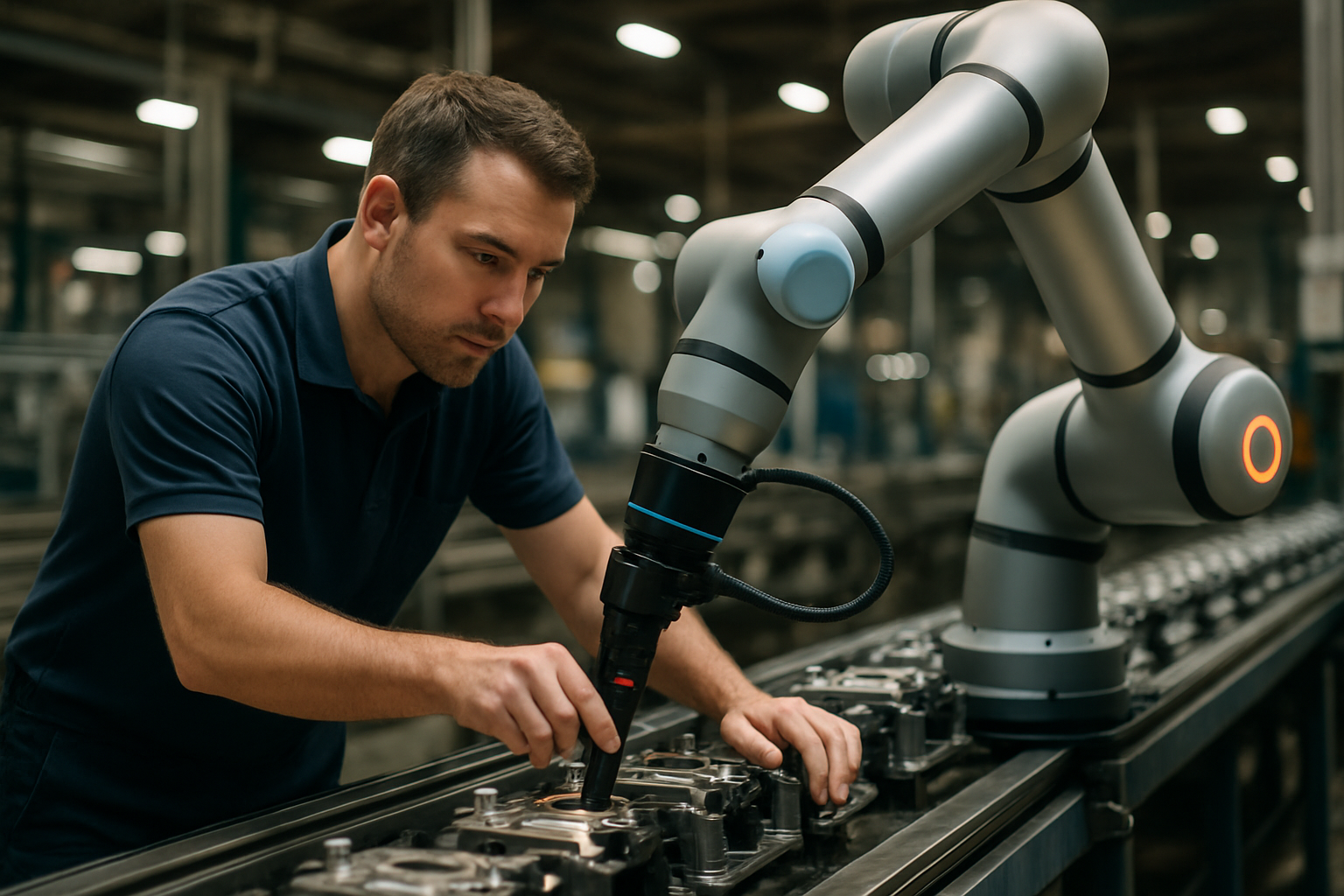

Historical Context and Evolution
Adaptive manufacturing has its roots in the early 20th century when Henry Ford revolutionized production with the assembly line. This marked the beginning of mass production, prioritizing efficiency and standardization. However, as consumer demands became more diverse, the limitations of rigid manufacturing systems became apparent.
The 1980s saw the emergence of lean manufacturing principles, emphasizing waste reduction and continuous improvement. This laid the groundwork for more flexible production systems. The advent of computer-integrated manufacturing in the 1990s further enhanced flexibility, but true adaptability remained elusive.
The rise of Industry 4.0 in the 21st century, characterized by interconnected systems and data-driven decision-making, has finally made adaptive manufacturing a reality. Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and additive manufacturing have converged to create truly flexible and responsive production systems.
Key Components of Adaptive Manufacturing
Adaptive manufacturing relies on several critical components that work in harmony to create a responsive and efficient production ecosystem:
-
Flexible Automation: Unlike traditional rigid automation, flexible automation systems can be quickly reconfigured to produce different products or accommodate process changes.
-
Advanced Sensing and Data Analytics: Real-time data collection and analysis enable continuous monitoring of production processes, allowing for immediate adjustments and optimizations.
-
Modular Production Units: These self-contained units can be easily rearranged or repurposed, allowing for rapid changes in production layout and capabilities.
-
Digital Twin Technology: Virtual representations of physical systems enable simulation and optimization of processes before implementation, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
-
Adaptive Control Systems: These systems use machine learning algorithms to continuously optimize production parameters based on real-time data and changing conditions.
Benefits and Challenges
Adaptive manufacturing offers numerous benefits to businesses, including:
-
Increased Responsiveness: Companies can quickly adapt to market changes and customer demands, reducing time-to-market for new products.
-
Enhanced Customization: The ability to efficiently produce small batches or even individual items allows for greater product personalization.
-
Improved Resource Utilization: Adaptive systems optimize resource allocation, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency.
-
Resilience to Disruptions: Flexible production systems can more easily adapt to supply chain disruptions or unexpected events.
However, implementing adaptive manufacturing also presents several challenges:
-
High Initial Investment: The advanced technologies required for adaptive manufacturing can be costly to implement.
-
Skill Gap: Workforce training is necessary to operate and maintain complex adaptive systems.
-
Data Security: The increased reliance on data and interconnected systems raises cybersecurity concerns.
-
Complexity Management: Balancing flexibility with operational stability requires sophisticated management systems.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Adaptive manufacturing is finding applications across various industries:
In the automotive sector, BMW has implemented an adaptive assembly line that can produce different models on the same line without interruption. This flexibility allows the company to respond quickly to changes in demand for specific models.
The aerospace industry is leveraging adaptive manufacturing for complex, low-volume parts. GE Aviation uses adaptive manufacturing techniques to produce fuel nozzles for jet engines, reducing the number of parts from 20 to 1 and improving fuel efficiency.
In the consumer goods sector, Adidas’ Speedfactory concept demonstrates how adaptive manufacturing can enable localized, on-demand production of customized products.
Future Trends and Implications
As adaptive manufacturing continues to evolve, several trends are emerging:
-
Hyper-personalization: Advances in adaptive manufacturing will enable cost-effective production of highly personalized products at scale.
-
Distributed Manufacturing: Adaptive systems will facilitate the development of smaller, localized production facilities closer to end consumers.
-
Sustainability Focus: The flexibility of adaptive manufacturing will support more sustainable practices, such as on-demand production and easier implementation of circular economy principles.
-
AI-driven Optimization: Machine learning algorithms will play an increasingly crucial role in optimizing adaptive manufacturing systems in real-time.
Implementing Adaptive Manufacturing: Key Considerations
• Conduct a thorough assessment of current production processes to identify areas for improvement
• Invest in workforce development to ensure employees are equipped to operate new technologies
• Start with pilot projects to test adaptive manufacturing concepts before full-scale implementation
• Develop a robust data strategy to leverage the full potential of adaptive systems
• Collaborate with technology providers and industry partners to stay abreast of latest developments
In conclusion, adaptive manufacturing represents a significant leap forward in industrial production capabilities. By combining flexibility, efficiency, and customization, it offers businesses a powerful tool to navigate the complexities of modern markets. As technology continues to advance and consumer expectations evolve, adaptive manufacturing will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping the future of industry. Companies that successfully implement these systems will be well-positioned to thrive in an era of rapid change and uncertainty.