Dolphin-Assisted Therapy: Exploring Aquatic Healing
In the realm of unconventional therapies, dolphin-assisted treatment has emerged as a captivating and controversial approach to healing. This unique form of therapy combines the soothing properties of water with the alleged therapeutic benefits of interacting with dolphins. As interest in alternative therapies grows, dolphin-assisted treatment has garnered attention from both proponents and skeptics alike, sparking debates about its efficacy and ethical implications.
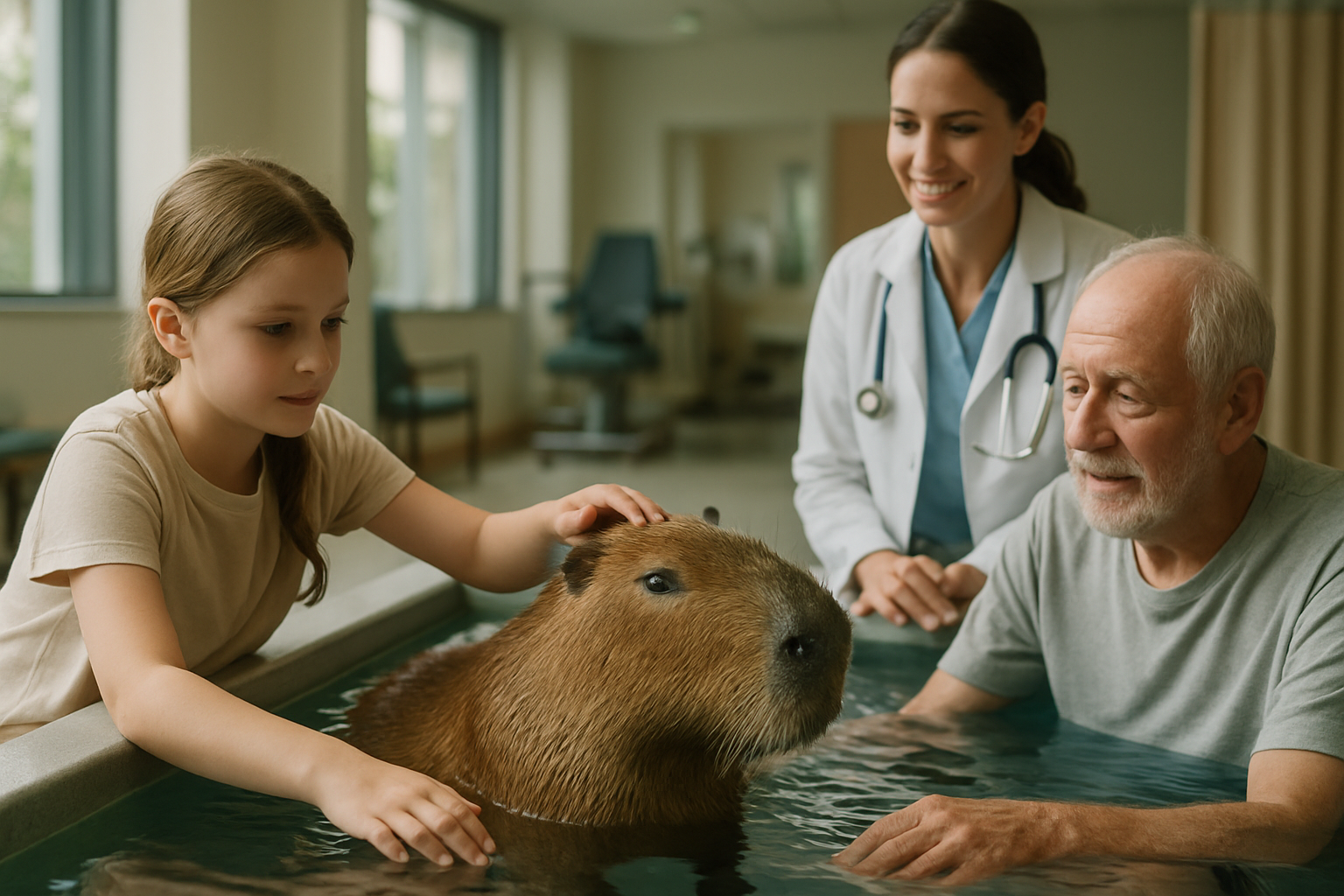

The Origins of Dolphin-Assisted Therapy
The concept of using dolphins for therapeutic purposes can be traced back to the 1970s. Dr. John Lilly, a neuroscientist and psychoanalyst, pioneered early research into dolphin-human interactions. His work, although controversial, laid the foundation for exploring the potential benefits of dolphin encounters on human well-being.
In the 1980s, Dr. David Nathanson began developing structured dolphin-assisted therapy programs. He hypothesized that interactions with dolphins could enhance motivation and attention in children with disabilities, potentially accelerating their learning processes. These early experiments marked the beginning of more formalized DAT programs.
The Proposed Benefits of Dolphin-Assisted Therapy
Advocates of dolphin-assisted therapy claim a wide range of benefits for participants. These purported advantages include improvements in:
-
Motor skills and physical rehabilitation
-
Cognitive function and learning abilities
-
Communication and language skills
-
Emotional well-being and stress reduction
-
Social interaction and behavior
Proponents argue that the unique combination of water-based activities and animal interaction creates a stimulating environment that can catalyze positive changes in patients. The calming effect of water, coupled with the novelty and excitement of dolphin encounters, is said to create an ideal setting for therapeutic interventions.
The Science Behind Dolphin-Assisted Therapy
While anecdotal evidence and individual case studies have reported positive outcomes, the scientific community remains skeptical about the effectiveness of dolphin-assisted therapy. Several factors contribute to the difficulty in scientifically validating DAT:
-
Limited controlled studies: The nature of DAT makes it challenging to conduct large-scale, randomized controlled trials, which are considered the gold standard in medical research.
-
Placebo effect: The excitement and novelty of interacting with dolphins may create a strong placebo effect, making it difficult to distinguish between genuine therapeutic benefits and temporary emotional uplift.
-
Multiple variables: DAT sessions often involve various elements, including water therapy, animal interaction, and traditional therapeutic techniques. Isolating the specific impact of dolphin interaction becomes problematic.
-
Lack of standardization: DAT programs vary widely in their approach, duration, and intensity, making it challenging to compare results across different studies and facilities.
Despite these challenges, some researchers have attempted to investigate the potential mechanisms behind DAT. One theory suggests that dolphin vocalization and echolocation may influence human brainwave patterns, potentially leading to therapeutic effects. However, this hypothesis remains largely unproven and controversial within the scientific community.
Ethical Considerations and Criticism
As interest in dolphin-assisted therapy has grown, so too have concerns about its ethical implications. Critics raise several important points:
-
Animal welfare: Keeping dolphins in captivity for therapeutic purposes raises questions about their well-being and natural behaviors.
-
Exploitation: Some argue that using dolphins for human therapy constitutes exploitation of intelligent and sentient beings.
-
Safety concerns: There are potential risks associated with close human-dolphin interactions, including accidental injuries to both patients and animals.
-
False hope: Critics worry that promoting DAT as a miracle cure may give false hope to individuals and families dealing with serious medical conditions.
-
Financial burden: DAT sessions can be expensive, with costs ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars per session, potentially placing a significant financial burden on patients and their families.
These ethical concerns have led to increased scrutiny of DAT programs and calls for stricter regulations and oversight.
The Future of Dolphin-Assisted Therapy
As the debate surrounding dolphin-assisted therapy continues, the future of this practice remains uncertain. Some countries have already implemented bans or strict regulations on dolphin captivity, which directly impacts the availability of DAT programs.
Researchers and practitioners are exploring alternative approaches that aim to capture the potential benefits of DAT while addressing ethical concerns. These include:
-
Virtual reality simulations: Using advanced technology to create immersive dolphin encounters without involving live animals.
-
Robotic dolphins: Developing lifelike robotic dolphins that can interact with patients in controlled environments.
-
Wild dolphin programs: Shifting focus to therapeutic encounters with free-ranging dolphins in their natural habitats, although this approach presents its own set of challenges and ethical considerations.
As the field evolves, it is clear that more rigorous scientific research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and limitations of dolphin-assisted therapy. Balancing the desire to explore innovative therapeutic approaches with ethical considerations and evidence-based practice will be crucial in shaping the future of this controversial treatment modality.
In conclusion, dolphin-assisted therapy remains a subject of fascination and debate within the medical and animal welfare communities. While some individuals report positive experiences, the lack of conclusive scientific evidence and persistent ethical concerns continue to cast doubt on its widespread adoption. As research progresses and alternative approaches are developed, the coming years will likely bring further insights into the complex relationship between human health and dolphin interactions.