Hydrogen Fuel Cells: The Quiet Revolution in Automotive Power
Imagine cruising down the highway in a car that emits nothing but water vapor, refuels in minutes, and offers a range comparable to gasoline-powered vehicles. This isn't science fiction—it's the promise of hydrogen fuel cell technology. As the automotive industry grapples with environmental concerns and the search for sustainable energy sources, hydrogen fuel cells are emerging as a compelling alternative to traditional combustion engines and battery-powered electric vehicles.
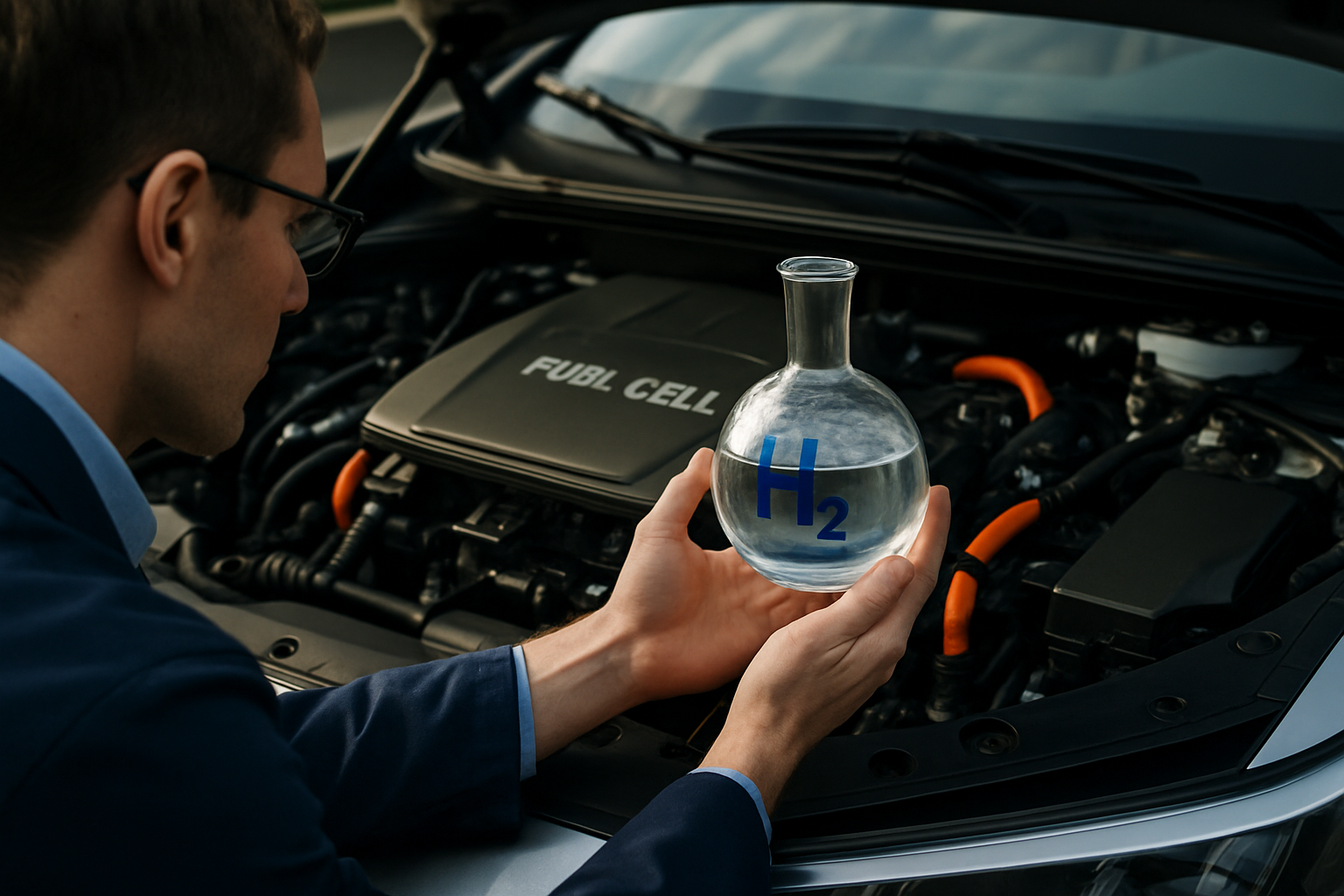

A Brief History of Hydrogen in Automotive Applications
The concept of using hydrogen as a fuel source dates back to the early 19th century, but it wasn’t until the 1960s that General Motors produced the first hydrogen fuel cell vehicle prototype. Progress was slow due to technological limitations and the high cost of fuel cell production. However, the past two decades have seen significant advancements, with major automakers like Toyota, Honda, and Hyundai bringing fuel cell vehicles to market.
Advantages Over Conventional and Battery Electric Vehicles
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer several advantages over both traditional internal combustion engines and battery electric vehicles. Unlike battery-powered cars, fuel cell vehicles can be refueled in a matter of minutes, similar to gasoline-powered cars. They also tend to have a longer range, with some models capable of traveling over 400 miles on a single tank of hydrogen. Additionally, fuel cells don’t degrade over time like batteries, potentially offering a longer lifespan for the powertrain.
Infrastructure Challenges and Solutions
One of the primary hurdles facing widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is the lack of refueling infrastructure. Unlike electricity, which is readily available, hydrogen refueling stations are scarce. However, several countries, including Japan, Germany, and parts of the United States, are investing heavily in building hydrogen infrastructure. Innovative solutions, such as on-site hydrogen production at fueling stations, are being developed to address this challenge.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
While hydrogen fuel cells themselves produce zero emissions, the environmental impact of hydrogen as a fuel source depends largely on how it’s produced. Currently, most hydrogen is derived from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming, which does produce carbon emissions. However, there’s growing interest in green hydrogen production methods, such as using renewable energy to power electrolysis of water. As these technologies advance, the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles could become even more significant.
Technological Advancements Driving Adoption
Recent years have seen remarkable progress in fuel cell technology. Improvements in catalyst design have reduced the amount of precious metals required, significantly lowering production costs. Advances in hydrogen storage systems have increased fuel capacity while reducing weight. Furthermore, innovations in fuel cell stack design have improved efficiency and durability, making fuel cell vehicles more practical for everyday use.
The Role of Government Policy and Industry Collaboration
Government support has been crucial in advancing hydrogen fuel cell technology. Countries like Japan and South Korea have set ambitious targets for fuel cell vehicle adoption and are offering substantial incentives to both consumers and manufacturers. In the United States, California has been at the forefront of promoting hydrogen technology through its Zero Emission Vehicle program. Industry collaboration has also played a vital role, with automakers forming partnerships to share development costs and accelerate technological progress.
Future Prospects and Market Outlook
While hydrogen fuel cell vehicles currently represent a small fraction of the automotive market, many industry experts predict significant growth in the coming decades. As production scales up and costs come down, fuel cell vehicles could become increasingly competitive with other powertrain technologies. Some analysts forecast that by 2050, hydrogen fuel cells could power up to 400 million cars, 15-20 million trucks, and around 5 million buses globally.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its promise, hydrogen fuel cell technology faces several challenges. Critics point to the inefficiency of hydrogen production and distribution compared to direct use of electricity in battery-powered vehicles. There are also concerns about the safety of hydrogen storage and transportation, although proponents argue that with proper safety measures, hydrogen is no more dangerous than other fuels. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for the widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles.
Implications for the Automotive Industry
The rise of hydrogen fuel cell technology could have far-reaching implications for the automotive industry. It may require significant retooling of manufacturing facilities and the development of new supply chains. For traditional automakers, mastering fuel cell technology could provide a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market. However, it also presents challenges, as companies must balance investments in multiple powertrain technologies to hedge against an uncertain future.
In conclusion, hydrogen fuel cell technology represents a fascinating frontier in automotive engineering. While challenges remain, the potential benefits in terms of performance, sustainability, and consumer convenience make it a compelling option for the future of transportation. As research continues and infrastructure expands, we may soon see hydrogen fuel cell vehicles playing a significant role in our transition to a cleaner, more sustainable automotive landscape.