The Hidden World of Axolotl Regeneration
Axolotls, the enigmatic salamanders of Mexico, have captivated scientists and animal enthusiasts alike with their extraordinary ability to regenerate lost body parts. This remarkable trait, unparalleled in the animal kingdom, has sparked a surge of interest in these aquatic amphibians. From regrowing limbs to repairing damaged organs, axolotls possess a regenerative prowess that could hold the key to revolutionary medical breakthroughs.
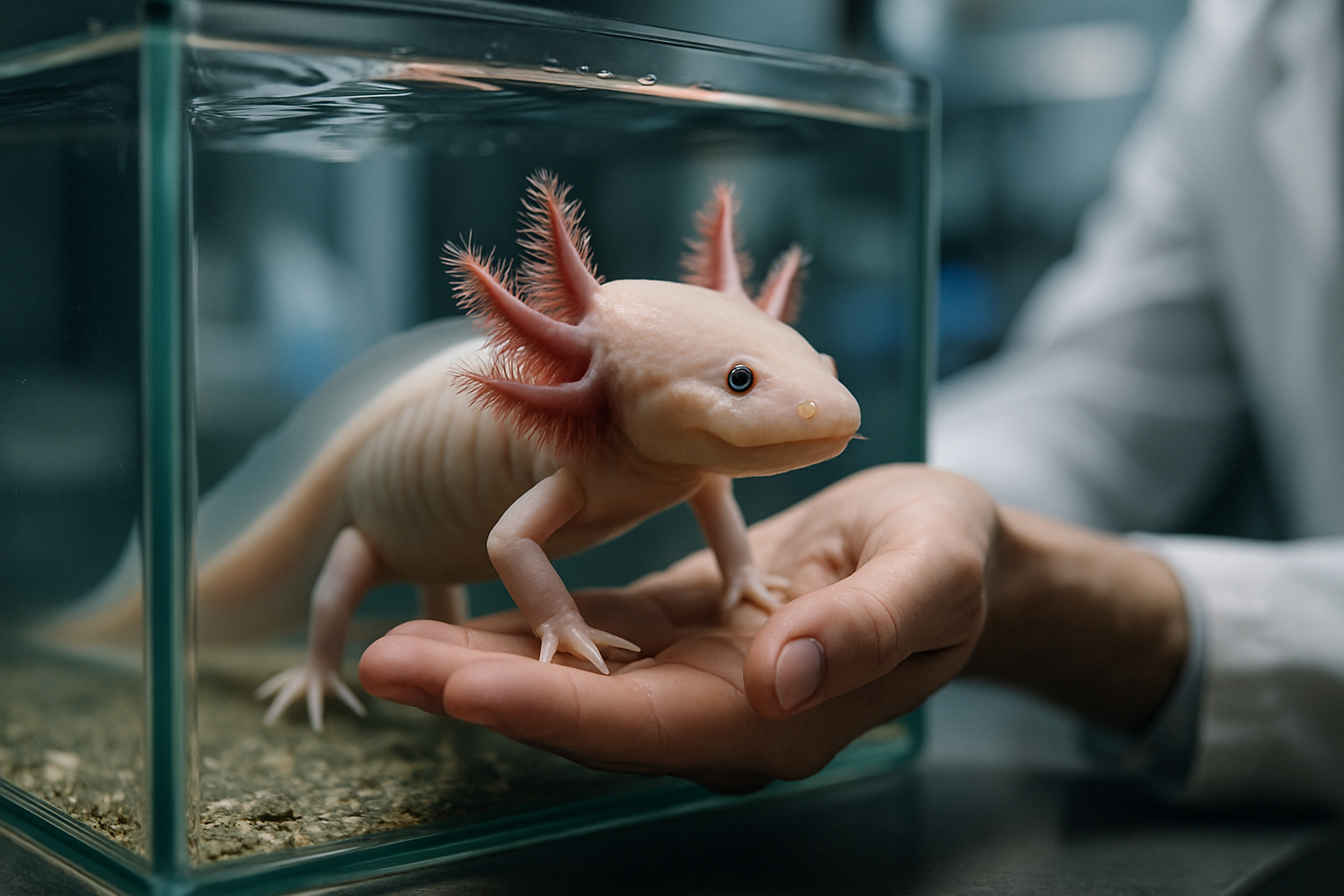

The Axolotl’s Evolutionary Journey
The axolotl’s story begins millions of years ago in the ancient lakes of Mexico. These unique salamanders evolved in isolation, developing their remarkable regenerative abilities as a survival mechanism. Unlike most amphibians, axolotls retain their larval features throughout adulthood, a phenomenon known as neoteny. This arrested development allows them to maintain the regenerative capabilities typically associated with embryonic stages.
Unraveling the Secrets of Regeneration
At the heart of the axolotl’s regenerative prowess lies a complex interplay of cellular processes. When an axolotl loses a limb, a mass of cells called a blastema forms at the site of injury. This blastema contains dedifferentiated cells that can transform into various cell types needed to rebuild the lost appendage. Scientists have identified key genes and signaling pathways involved in this process, shedding light on the molecular mechanisms driving regeneration.
Beyond Limb Regeneration
While the ability to regrow limbs is impressive, axolotls’ regenerative capabilities extend far beyond that. These remarkable creatures can repair damaged spinal cords, regenerate portions of their brain, and even reconstruct their heart tissue after injury. This comprehensive regenerative ability sets axolotls apart from other animals and has made them invaluable models for studying tissue repair and organ regeneration.
Implications for Human Medicine
The axolotl’s regenerative abilities have sparked excitement in the medical community, offering potential insights into human tissue repair and regeneration. Researchers are exploring ways to apply the principles of axolotl regeneration to develop new treatments for spinal cord injuries, heart disease, and other conditions involving tissue damage. While human regeneration on the scale of axolotls remains a distant goal, these studies are paving the way for innovative regenerative therapies.
Conservation Challenges and Captive Breeding
As fascinating as axolotls are to science, their wild populations face severe threats. Habitat loss, pollution, and the introduction of invasive species have pushed wild axolotls to the brink of extinction. Conservation efforts, including habitat restoration and captive breeding programs, are crucial for preserving these unique creatures. The estimated price range for a captive-bred axolotl in the pet trade varies from $20 to $70, depending on color morph and availability.
The Future of Axolotl Research
As technology advances, so does our understanding of axolotl regeneration. Cutting-edge techniques like single-cell RNA sequencing and CRISPR gene editing are providing unprecedented insights into the genetic and cellular mechanisms underlying regeneration. These tools are helping scientists identify key regulators of the regenerative process, bringing us closer to unlocking the secrets of tissue repair and regeneration.
Ethical Considerations in Axolotl Research
The use of axolotls in scientific research raises important ethical questions. While their regenerative abilities make them valuable research subjects, it’s crucial to ensure their welfare and minimize suffering. Many institutions have established guidelines for the ethical treatment of axolotls in laboratory settings, balancing the potential benefits of research with the well-being of these remarkable creatures.
Axolotls in Popular Culture
Beyond their scientific significance, axolotls have captured the public imagination, appearing in various forms of media and popular culture. From children’s books to video games, these smiling salamanders have become iconic symbols of regeneration and resilience. This cultural presence has helped raise awareness about axolotls and their conservation needs, inspiring a new generation of enthusiasts and potential researchers.
In conclusion, the hidden world of axolotl regeneration continues to amaze and inspire. As we unravel the mysteries behind their extraordinary abilities, we edge closer to potential breakthroughs in regenerative medicine. However, it’s crucial to remember that these remarkable creatures are more than just scientific curiosities. They are a unique part of our planet’s biodiversity, deserving of our protection and admiration. The story of the axolotl serves as a powerful reminder of nature’s ingenuity and the endless possibilities that arise when we look to the natural world for inspiration and solutions.